Patent infringement is the use a patent for commercial purposes without the patent holder’s permission. Patent infringement analysis determines the category of patent infringement. It is basically of two types- Literal infringement and Doctrine of equivalents.
Literal infringements: It occurs when the accused firm copies the product as claimed in the patent. Two main parameters of literal infringement are:
- The function of the accused product is similar to the original patent.
- It is also similar in terms of material and structure.
The doctrine of equivalents: This covers any partial infringement; if some part of the accused product is achieving the same result through the same process then it comes under the doctrine of equivalents.
Related article: Proofreading essentials: “The essential eight”
Steps of patent infringement analysis
The steps for a patent infringement analysis are:
- Interpret the claim in patent thoroughly.
- Compare the claims and accused product to check for literal infringements.
- In case of no literal infringement, check for infringement under the doctrine of equivalents.
The approach is to go in details of the claim as much as possible. In some cases, the whole drawing is similar and any small part is claimed. The accused product can have many similarities with the original patent but In case it’s not violating the claim, It doesn’t fall under patent infringement.
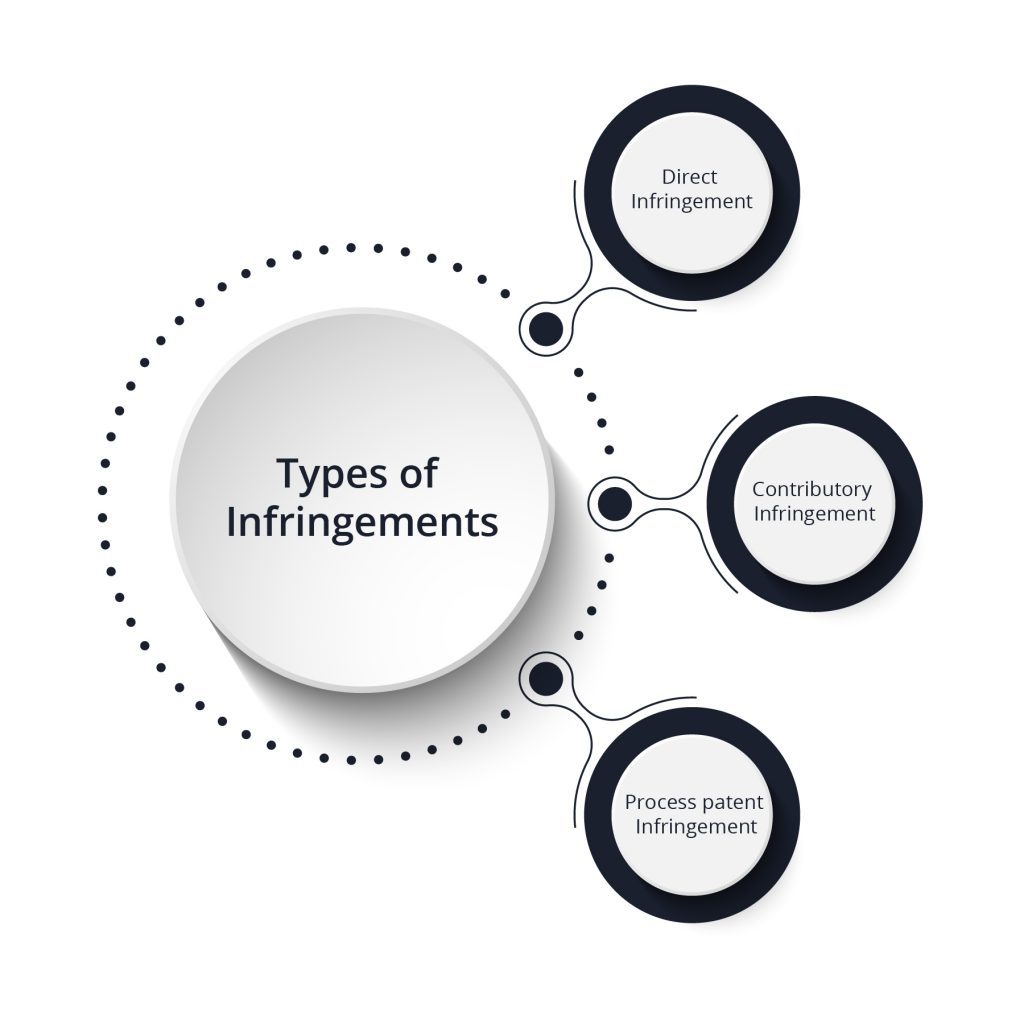
Types of infringements
Apart from literal infringement and the doctrine of equivalents, there are few more types of infringement based on the different violations.
- Direct infringement: If someone sells, uses, or offers to sell a patent in U.S.A without any authorisation comes under direct infringement.
- Contributory infringement: Copying a part from a patented invention and then use, sell or offer to sell it comes under this category of infringement
- Process patent infringement: Importing an invention in the U.S without the permission patent owner comes under process patent infringement.
Related article: Why proofread a patent?
Litigation process after patent infringement analysis
Once the patent infringement analysis is complete, Courts have a two-step process to determine the result.
- Claim construction
- The court rules whether the accused product infringes on the original patent.
Claim construction is the scenario when the court interprets the claims made in patent. During this process, the literal meaning of the term is considered. However, it can be changed if the patent owner gave a separate or special meaning to the term. Large firms focus on preparing a patent claim construction to strengthen their position on the legal front.
The court judges the product based on functionality. Any element in the claim is considered as a step or way to complete a function. It finishes the scope of the claim. If a meaning for a technical term is not clear, the court considers the meaning given by experts or textbooks. In conclusion, Claim construction is solely under the court however parties can have a jury trial questioning court’s interpretation of patent infringement. Moreover, there are certain ways to defend a patent infringement lawsuit.
Want to conduct a patent infringement analysis?
The Patent search firm has more than 8 years of experience in the IP field. Our team covers possibly every technical domain. Moreover, we have over 1200+ happy clients in 45+ countries. We go through every database to deliver precise results. Also, the clients can check the status of the work at any stage of the process. Moreover, 100 % customer satisfaction is our top priority. To know more, visit our service page: The Patent Search Firm.
